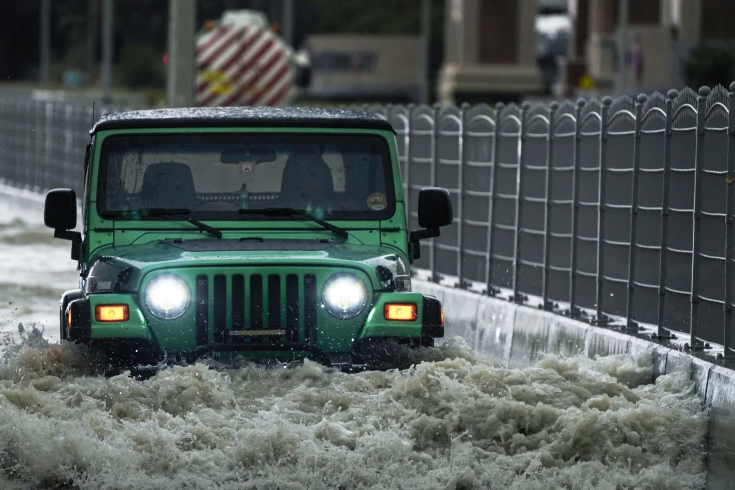
In a city known for its towering skyscrapers, opulent lifestyle, and arid climate, Dubai experienced an unexpected turn of events recently as torrential rains inundated the streets, causing widespread flooding. The deluge caught residents and authorities off guard, highlighting the vulnerability of even the most meticulously planned urban landscapes to the whims of nature.
The Deluge Unfolds
Dubai, nestled along the Persian Gulf coast, typically experiences a desert climate characterised by scorching temperatures and minimal rainfall. However, in recent years, irregular weather patterns attributed to climate change have disrupted this norm, occasionally bringing heavy downpours to the region.
The recent bout of flooding left many parts of the city submerged, disrupting traffic, causing property damage, and prompting emergency rescue operations. Videos circulated on social media depicted cars navigating through waterlogged streets reminiscent of Venice, while pedestrians waded through knee-deep water, struggling to reach their destinations.
@tonyz.777 Unbelivable😱 #Dubai #uae #dubaimall #dubaiflood #dubaiflood2024 #dubaistorm #dubairain ♬ original sound – tonyz777
Unveiling Cloud Seeding
In response to such weather anomalies, Dubai has been employing innovative techniques to mitigate the impact of drought and enhance rainfall. One such method gaining attention is cloud seeding, a process that involves dispersing substances into the atmosphere to encourage precipitation.
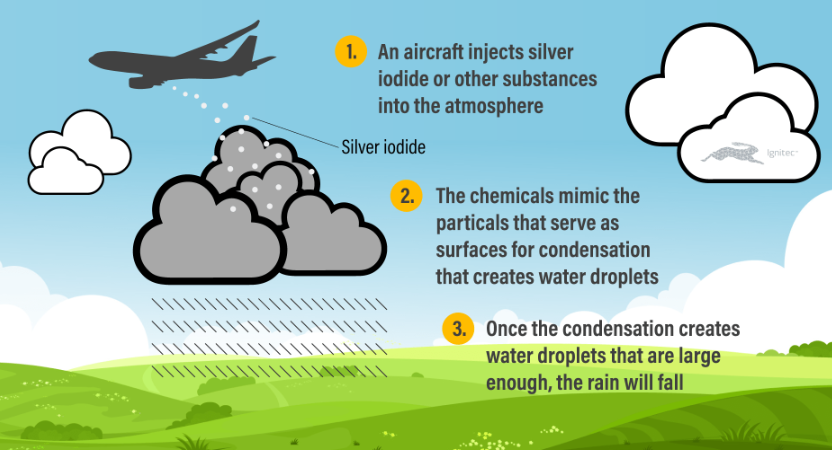
Cloud seeding operates on the principle of nucleation, where certain substances, typically silver iodide or potassium iodide, are released into clouds. These particles serve as nuclei around which water droplets condense, ultimately leading to the formation of raindrops. By artificially stimulating cloud formation and rainfall, cloud seeding offers a potential means of augmenting water resources in regions facing water scarcity.
Dubai’s Cloud Seeding Initiative
Dubai’s foray into cloud seeding is part of a broader strategy to address water security challenges in the face of climate change. The city’s meteorological department collaborates with specialized companies equipped with aircraft and ground-based generators to execute cloud seeding operations.
The process typically begins with the identification of suitable cloud formations conducive to seeding. Once target clouds are identified, aircraft equipped with dispensers release the seeding agents into the atmosphere. These agents disperse and interact with the clouds, enhancing the likelihood of precipitation.
Effectiveness and Controversies
While proponents of cloud seeding extol its potential to augment rainfall and alleviate drought conditions, skeptics raise concerns regarding its effectiveness and environmental implications. Critics argue that the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of cloud seeding remains inconclusive, with uncertainties surrounding its long-term impact on weather patterns and ecosystems.
Moreover, questions persist regarding the equitable distribution of water resources, with some fearing that cloud seeding may exacerbate disparities by favoring certain regions or industries over others. As such, calls for comprehensive research and transparent governance accompany discussions surrounding the expansion of cloud seeding initiatives.
A Balancing Act
The recent flooding in Dubai serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictability of nature and the imperative of proactive measures to adapt to changing climatic conditions. While cloud seeding represents a promising tool in the arsenal of water management strategies, its deployment warrants careful consideration, taking into account scientific evidence, environmental sustainability, and socio-economic equity.
As Dubai navigates the aftermath of the floods and charts its course towards a more resilient future, the role of innovative technologies like cloud seeding underscores the need for holistic approaches to address the complex challenges posed by climate change. In the face of adversity, innovation and collaboration emerge as indispensable allies in safeguarding the well-being of communities and ecosystems alike.